10
Nov 2025
13:00 UTC
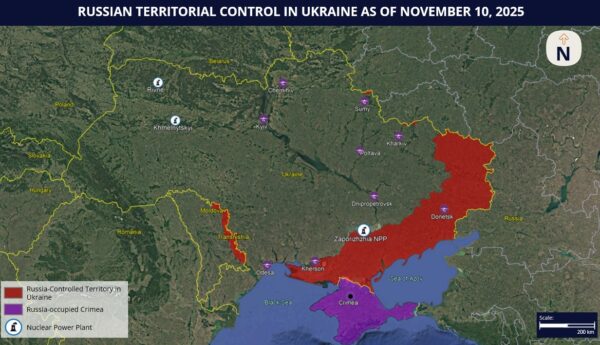
Russia & Ukraine SITUATION UPDATE: Russian airstrikes target critical energy infrastructure across Ukraine including Chernihiv; Russia passes reservist recruitment law as of November 9; rolling power outages, strikes likely to persist in Ukraine
Current Situation
Ukraine
Eastern Ukraine
- Per November 9 reports, Russian forces have continued offensive operations in Pokrovsk, Donetsk region, conducting house-to-house fighting and claiming to have captured several buildings. Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces of Ukraine Oleksandr Syrskyi stated that while the intensity of Russian attacks in the Pokrovsk area has decreased, Ukrainian defensive operations continue, and contingency plans have been prepared to maintain control of the area. Per Syrskyi, Pokrovsk is a continuous fortified area.
- Meanwhile, on November 6, Russia tried to advance in the Pokrovsk direction 55 times. Attacks were recorded in the areas of Chervonyi Lyman, Fedorivka, Myrnohrad, Nykanorivka, Rodynske, Dorozhnye, Novopavlivka, Novoekonomichne, Lysivka, Pokrovsk, Kotlyne, Udachne, Molodetske, and Filia.
- Also, on November 6, Russian strikes were recorded against railway infrastructure in the eastern regions of Ukraine, leading to changed routes for several trains. Per reports, the Zaporizhzhia-Kamianske station in the Dnipropetrovsk region was hit.
- Per the commander of the Forces of Unmanned Systems of the Armed Forces of Ukraine, Robert Brovdi, on November 6, Ukrainian forces destroyed the storage and launch base of Shahed-type attack UAVs in the temporarily occupied Donetsk.
Kyiv, Central, & Northern Ukraine
- As of November 10, Ukrainian authorities implemented nationwide rolling power outages following Russian strikes on energy infrastructure on November 8. According to Ukrenergo, restrictions will remain in effect across all regions throughout the day. In Kyiv, DTEK announced scheduled blackouts lasting up to 30 minutes per round, affecting all districts of the capital. The outages are to stabilize the power system and repair damage caused by earlier Russian UAV attacks targeting energy facilities.
- During the early morning hours (local time) of November 8, Russian strikes hit two thermal power plants supplying Kyiv and Kharkiv, leading to complete power outages until November 9.
- During the night hours of November 8, Russia launched 458 UAVs and 45 missiles, including ballistic missiles. Strikes were recorded in Kyiv, Kharkiv, Dnipropetrovsk, Odesa, and Poltava regions. Per reports, the strikes largely targeted energy infrastructure, reducing Ukraine’s power-generating capacity to “zero”. A civilian minibus was struck near Druzhkivka in Kindrativka village in the Donetsk region, injuring three. At least 16 civilians were killed in the Donetsk and Kherson regions.
- This followed Russian strikes targeting energy infrastructure in the Chernihiv region during the overnight hours of November 8–9, with at least 73 explosions recorded. During the overnight hours of November 5–6, Russian forces launched multiple airstrikes primarily targeting energy infrastructure in the Chernihiv region. Local authorities reported 104 explosions resulting from at least 35 strike events across 17 settlements. A power facility in a border community sustained significant damage, causing power outages and fire at the site. Additional strikes damaged transport infrastructure in the Nizhyn district and a residential building and a vehicle in the Koriukivka district.
- On November 9, Russian UAVs struck Romny, Sumy region, damaging warehouse premises of local businesses and shattering windows of a five-storey residential building.
- Also, on November 8, a Russian UAV struck a vehicle belonging to the humanitarian mission. The vehicle carried two foreign journalists from Austria and Spain and the mission’s volunteers, and no injuries were reported.
- On November 7, Russian strikes in Zaporizhzhia city led to structural damage to residential buildings and a kindergarten. During the night hours on November 7, Russian strikes hit a post office in Chuhuiv, Kharkiv region.
- Per November 6 reports, Russian strikes cut electricity to eight coal mines in the Dnipropetrovsk region, leaving approximately 2,600 miners trapped underground. On November 6, the Defence Forces of Ukraine denied claims made by the Russian forces about having seized territories in the Dnipropetrovsk and Zaporizhzhia regions.
- On November 7, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Director General Rafael Grossi stated that a local ceasefire was established near the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant to permit repairs on the damaged 330 kV “Ferrosplavna-1” power line, which had been offline for six months.
- On November 7, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy announced the launch of a program designed to protect frontline towns from Russian UAVs, including Kherson city.
- During the morning hours of November 9, Russian forces attacked the southern part of the Odesa region with UAVs. Local officials reported damage to several private garages and broken windows in a multi-story residential building. Meanwhile, on the same date, 34 Russian UAVs were intercepted in northern and eastern Ukraine.
- Per November 9 reports, Russian forces operating in the vicinity of Sumy continued to suffer losses due to desertion and inadequate training, with no tactical gains.
- On November 9, the Russian Ministry of Defense reported that its forces had captured the settlement of Volchye in the Dnipropetrovsk region. According to Russian state media, Russian forces eliminated retreating Ukrainian troops using weapons reportedly seized from Ukrainian positions in Volchye.
Crimea & Southern Ukraine
- During the night hours (local time) of November 6, units of the Special Operations Forces of the Armed Forces of Ukraine (SOF) struck Hvardiyska oil depot near the village of Gvardiysk in Russia-occupied Crimea, destroying a fuel tank and hitting two trains loaded with oil products. Additionally, the SOF destroyed an S‑400 Triumph missile launcher in the village of Uyutne near Yevpatoria and a large ammunition depot belonging to Russia in Udachne village near Simferopol.
- On November 9, ATESH, a Ukrainian Crimean Tatar partisan group, conducted a sabotage operation in the Russian-occupied Crimea region on a railway line near Simferopol, temporarily disrupting Russian military logistics by blocking train movements of ammunition, fuel, and equipment.
Other Military Developments
- On November 7, President Zelenskyy stated that Russian forces are accumulating large numbers of UAVs and preparing for new large-scale strikes against Ukraine’s critical infrastructure. Further, Zelenskyy stated that Ukraine is preparing for potential disruptions in gas supply and plans to import gas worth around two billion USD to ensure stability. He emphasized that Russia is currently not using its full strike capacity, with the ability to launch up to 500 UAVs per day and urged continued partner support.
- On November 9, President Zelenskyy stated that Ukraine plans to order 27 Patriot air defense systems from the USA while also considering borrowing similar systems from European countries.
- Russian state media, citing Russian law enforcement, reported on November 8 that at least 21,602 Ukrainian troops deserted their units in October, surpassing the May figures of 19,900.
- Following the November 8 Russian strikes against energy facilities, Ukraine’s First Deputy Minister of Energy Artem Nekrasov reported that Russia has shifted tactics to strike both electricity generation and distribution simultaneously.
Other Developments
- On November 6, the cement industry members called on the government to provide budget support instead of passing increased rail freight tariffs to businesses. They warned that a proposed 37 percent tariff hike by Ukrzaliznytsia, Ukrainian Railways, would affect the economy as two-thirds of cement produced in Ukraine is transported by rail.
- On 6 November, a court in Zaporizhzhia sentenced a Russian soldier to life in prison after finding him guilty of killing a Ukrainian Prisoner of War, who had surrendered in January 2024. The ruling is the first time Ukraine has handed down a custodial sentence for this type of war-crime charge since Russia’s 2022 invasion.
- During the night hours of November 8, Russian forces carried out a targeted attack on substations supplying Khmelnytskyi and Rivne nuclear power plants. According to Ukrainian Foreign Minister Andriy Sibiha, the infrastructure hit included key high-voltage substations, and that Russia was “deliberately jeopardizing the nuclear safety of Europe”.
- The IAEA, per November 9 reports, stated that nuclear safety in Ukraine remains critically unstable following Russian attacks. This is after the IAEA noted that two operational power plants in Khmelnytskyi and Rivne were forced to reduce electricity output after a Russian strike hit a high-voltage substation crucial to nuclear safety.
- On November 9, President Zelensky signed two decrees introducing new “special” sanctions against Russian government officials, financiers, collaborators, and propaganda entities. The measures target individuals involved in “looting” Ukrainian assets in occupied territories, spreading Russian narratives, and legitimizing their occupation.
Diplomatic and International Updates
- On November 8, Lithuanian and EU officials held discussions regarding the 20th sanctions package against Russia, which will also reportedly target Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko.
- As per November 9 reports, the ongoing US Federal Government shutdown has led to delays in weapons export to Ukraine and NATO allies, amounting to approximately five billion USD. Delays include deliveries of the HIMARS rocket system and the Aegis weapons system for military deals with Croatia, Denmark, and Poland.
- On November 7, US President Donald Trump received Hungarian President Viktor Orban in Washington and stated that there is a “very good chance” of meeting Russian President Vladimir Putin during the proposed US-Hungary summit in Budapest, Hungary. Additionally, Trump also stated his intentions of meeting Central Asian leaders at the White House as part of resolving the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Russia
- Between November 6 and 9, energy infrastructure at multiple locations was targeted by Ukrainian UAV attacks, leading to significant damage and blackouts. This included an attack on an oil refinery in Volgograd, which also killed an individual, and the Kostroma Power Station in the Kostroma Region. Airstrikes also targeted the thermal power station in Belgorod, an energy plant in Taganrog, and a petrochemical plant in the Republic of Bashkortostan. The strikes led to significant disruptions in electricity, mobile communications, and water supply services.
- Russian air defense units claimed to have shot down 75 Ukrainian UAVs across several regions during this period, most in Volgograd, and intercepted seven HIMARS rockets and over 200 UAVs between November 8–9.
- On November 8, around 10 explosions were reported in the Saratov region during early morning hours, which led to the temporary closure of the Saratov Gagarin Airport (GSV). The city has a specialized refinery facility and the Engels-2 military airbase.
- As per November 5 reports, Russia has suspended fuel exports from the Black Sea port of Tuapse, Krasnodar Krai, after a Ukrainian UAV strike significantly damaged a refinery located at the port on November 2. The strike also led to an oil spill extending over 3 kilometers from the terminal.
- Separately, reports on November 9 indicated that anti-government resistance groups destroyed four Russian military logistics facilities in late October and early November, including three communication towers in Sterlitamak and a railway control cabinet near the Vologda region. In Voronezh, three explosions caused temporary blackouts after a partisan group called ATESH reportedly shared intelligence on local energy sites with Ukrainian authorities.
- On November 4, Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a law enabling reservists, who are part of the Boyevoy Armeyskiy Rezerv Strany (BARS), a Russian military reserve force, to be trained for protecting domestic critical infrastructure, including energy and transport, against UAV attacks. Around 15 regional governments are reportedly actively recruiting reservists under the new law, and the role includes benefits related to pay and healthcare.
- Separately, on November 4, Putin signed a law for a year-round conscription, allowing military draft boards to conduct enlistment procedures, besides intakes, at any time throughout the year, starting January 2026.
- As per November 9 reports, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has approved a new security resolution sanctioning senior Russian officials, including Kirill Dmitriev, CEO of the Russian Direct Investment Fund (RDIF), and Oxana Lut, Minister of Agriculture, as well as five Russian publishing houses.
- As per November 8 reports, Zelenskyy stated that October 2025 saw the highest Russian troop losses since the start of the war, with over 25,000 soldiers killed, largely due to intensified drone strikes. Ukraine’s General Staff estimates Russia’s total losses since February 2022 at around 1.15 million personnel, along with more than 11,000 tanks and 23,000 armored vehicles.
- On November 7, Ukraine’s Foreign Ministry claimed that over 1,000 citizens from 36 African countries are serving in the Russian army, allegedly through coercion or for payment. It also reported that about 10,000 troops of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), also known as North Korea, have been deployed near Russia’s border with Ukraine, with another 5,000 North Koreans assisting in infrastructure repairs. These reports followed talks between Russian and North Korean officials on November 6 to deepen bilateral cooperation.
Assessments & Forecast
Ukraine
- The November 8–9 Russian strikes on Ukrainian energy infrastructure are consistent with Moscow’s established strategy of degrading Ukraine’s energy generation and transmission capacity ahead of winter. The attacks followed earlier strikes on power substations and a gas processing facility on October 29–30, indicating a sustained campaign aimed at overwhelming repair capacity and destabilizing essential services. The focus on substations supplying power to nuclear facilities further highlights Russia’s intent to disrupt not only national energy output but also critical grid stability.
- FORECAST: Given reports that multiple generation sites were rendered inoperative, rolling power outages across Ukraine are expected to persist in the near term, affecting essential services such as water supply, telecommunications, and public transport. Recovery is likely to remain slow due to limited repair capacity and ongoing security risks for maintenance crews. Moscow is expected to exploit the current grid instability with renewed large-scale strikes on high-value energy nodes, including substations and gas infrastructure, to sustain civilian hardship and strain Ukraine’s emergency response capacity. As winter progresses, Russia is also likely to intensify precision strikes on distribution systems, including substations supporting nuclear power plants.
- The ongoing Russian offensive in Pokrovsk aligns with Moscow’s broader campaign to secure full control of the Donetsk region. The reported house-to-house fighting indicates that Russian forces have entered the urban perimeter, suggesting they have established a partial foothold within the city. Syrskyi’s characterization of Pokrovsk as a “continuous fortified area” underscores that Ukrainian defenses are deeply entrenched and structured to absorb prolonged attritional fighting, consistent with the defensive posture observed across other contested sectors of Donetsk since late October.
- FORECAST: Consequently, Russian forces are likely to intensify ground operations in Pokrovsk in the coming days, following current logistical buildup and forward troop rotations. The reported redeployment of up to 170,000 Russian troops to the Pokrovsk sector and the use of infiltration groups, FPV UAVs, and indirect fire indicate that Moscow is preparing for a high-intensity, multi-axis assault aimed at encircling Pokrovsk and collapsing Ukraine’s broader defensive “fortress belt” anchored around Kramatorsk and Sloviansk. Current Russian positions in the southern and eastern parts of Pokrovsk, alongside reported control of nearby settlements such as Rodynske and Myrnohrad, allow Moscow to gradually constrict Ukrainian logistics and apply sustained pressure on defensive lines. However, Russian gains will likely remain slow and attritional, constrained by heavy urban resistance, overstretched logistics, and weather-related operational limitations.
- Meanwhile, the cement industry’s warning over Ukrzaliznytsia’s proposed 37 percent rail freight tariff increase underscores broader economic risks for Ukraine’s industrial and construction sectors. As roughly two-thirds of domestic cement is transported by rail, higher tariffs would directly raise operational costs, potentially leading to moderate price increases for construction materials and reduced production rates. Similar cost pressures may emerge for other rail-dependent industries, including steel and grain producers.
Russia
- The decision to deploy reservists from the BARS to guard critical infrastructure highlights Russia’s intent to establish a specialized domestic protection force amid persistent Ukrainian UAV attacks. This development reflects ongoing manpower shortages across the Russian military, already underscored by the new law permitting year-round conscription from January 2026. The initiative appears designed to free up frontline units for offensive operations in Ukraine while ensuring continued protection of key domestic assets, particularly energy and transport infrastructure that has come under repeated attacks in recent months.
- FORECAST: While the formation of such a force demonstrates Russia’s adaptation to the evolving threat environment, the BARS program’s reliance on part-time reservists suggests that training delays, coordination challenges, and logistical shortfalls will limit the immediate operational value of this force. Moreover, integrating reservists into roles traditionally managed by security services, like Rosgvardiya and FSB, increases the risk of jurisdictional overlap and inefficiencies. As such, in the immediate-to-near term, disruptions from UAV strikes on energy and transport networks are expected to continue. Nonetheless, by mid-to-late 2026, the program is likely to enhance localized protection around high-value targets, especially in strategic regions such as Moscow, Rostov, and Belgorod, supported by improved counter-UAV systems.
- In addition to expanding reservist programs and implementing year-round conscription, Russia’s persistent manpower constraints are further evidenced by the reports of African and North Korean personnel serving with Russian forces. This aligns with Moscow’s broader strategy of sourcing manpower from allied or economically dependent states for combat, support, and intelligence roles. However, given precedent, these deployments are unlikely to deliver significant battlefield gains, as most foreign recruits lack advanced training, language compatibility, and familiarity with Russian command structures and equipment. Their roles are therefore expected to remain largely auxiliary, focused on logistics, construction, or rear-area duties.
- FORECAST: Moscow’s efforts to implement year-round conscription are likely to fuel sporadic backlash in the form of localized protests, vandalism, and arson attacks on military enlistment offices, particularly as public fatigue with the war deepens. Based on precedent, the Kremlin is expected to prioritize recruitment in economically disadvantaged regions, such as the North Caucasus, Siberia, and the Far East, where state dependence and limited employment opportunities make resistance more manageable. However, this approach also heightens the risk of localized unrest and ethnic tensions, especially in areas like Dagestan and Buryatia, which have already recorded prior instances of anti-draft demonstrations. While widespread mobilization protests remain unlikely due to tight state controls, isolated acts of defiance and sabotage against recruitment infrastructure are expected to persist through 2026.
Recommendations
Ukraine
- Avoid all travel to Ukraine due to the ongoing hostilities.
- Those operating in the East, South, and Center of Ukraine are advised to minimize outdoor travel and avoid inter-city travel due to the increase in artillery fire and airstrikes.
- Avoid all travel to Crimea due to the ongoing conflict and the potential for sporadic attacks on civilian and critical infrastructure facilities.
- Those continuing to operate in the North and West of Ukraine are advised to adhere to air raid sirens over the coming days due to the heightened threat of missile and UAV attacks by Russian forces.
- Identify the nearest shelter, which may be a Metro station, and proceed towards it when air sirens are sounded. Prepare emergency kits of food, water, medicine, and clothing in case needed.
- Considering the heightened risk of unpredictable power outages, take mitigatory measures, such as confirming that business locations have working generators, sufficient access to fuel for longer periods, and access to several flashlights. Keep necessary electronics constantly charged.
- For more information on the security situation and assistance please contact [email protected]
Russia
- Avoid nonessential travel to Russia due to potential instability in the coming days, the underlying threat of military mobilization, arbitrary detention, and increased risk of spillover violence in regions bordering Ukraine.
- Remain cognizant of authorities’ updates regarding travel prohibitions on individuals deemed eligible for military conscription.
- Foreign companies operating in Russia are advised to remain cognizant of government regulations and decrees that pose risks to business continuity and operations.
- It is recommended to have emergency plans in place in case of further deterioration in the security landscape.
- Foreign citizens in Moscow and other areas in western Russia are advised to review evacuation plans in case of emergencies.
- Avoid all travel in the vicinity of government and military facilities, as well as possible political gatherings or lone picket protests, in the coming days.
- Remain cognizant of restrictions enacted at a regional and local level.
- Avoid discussions concerning the political, economic, and military situation, even with friends and family.
- Avoid meeting strangers, discussing the political situation, or using any anti-Russia rhetoric in public.
- Those intending to travel between Russia and its neighboring European countries are advised to remain cognizant of authorities’ updates regarding land border restrictions. Review options for departing Russia, including air, rail, and land routes, with the understanding that certain options may become unavailable with short notice.
COUNTRY RISK LEVEL
Extreme
AFFECTED AREA
Russia & Ukraine
INCIDENT RISK LEVEL
Extreme
STRENGTH OF SOURCE
Credible
Current Situation
Ukraine
Eastern Ukraine
- Per November 9 reports, Russian forces have continued offensive operations in Pokrovsk, Donetsk region, conducting house-to-house fighting and claiming to have captured several buildings. Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces of Ukraine Oleksandr Syrskyi stated that while the intensity of Russian attacks in the Pokrovsk area has decreased, Ukrainian defensive operations continue, and contingency plans have been prepared to maintain control of the area. Per Syrskyi, Pokrovsk is a continuous fortified area.
- Meanwhile, on November 6, Russia tried to advance in the Pokrovsk direction 55 times. Attacks were recorded in the areas of Chervonyi Lyman, Fedorivka, Myrnohrad, Nykanorivka, Rodynske, Dorozhnye, Novopavlivka, Novoekonomichne, Lysivka, Pokrovsk, Kotlyne, Udachne, Molodetske, and Filia.
- Also, on November 6, Russian strikes were recorded against railway infrastructure in the eastern regions of Ukraine, leading to changed routes for several trains. Per reports, the Zaporizhzhia-Kamianske station in the Dnipropetrovsk region was hit.
- Per the commander of the Forces of Unmanned Systems of the Armed Forces of Ukraine, Robert Brovdi, on November 6, Ukrainian forces destroyed the storage and launch base of Shahed-type attack UAVs in the temporarily occupied Donetsk.
Kyiv, Central, & Northern Ukraine
- As of November 10, Ukrainian authorities implemented nationwide rolling power outages following Russian strikes on energy infrastructure on November 8. According to Ukrenergo, restrictions will remain in effect across all regions throughout the day. In Kyiv, DTEK announced scheduled blackouts lasting up to 30 minutes per round, affecting all districts of the capital. The outages are to stabilize the power system and repair damage caused by earlier Russian UAV attacks targeting energy facilities.
- During the early morning hours (local time) of November 8, Russian strikes hit two thermal power plants supplying Kyiv and Kharkiv, leading to complete power outages until November 9.
- During the night hours of November 8, Russia launched 458 UAVs and 45 missiles, including ballistic missiles. Strikes were recorded in Kyiv, Kharkiv, Dnipropetrovsk, Odesa, and Poltava regions. Per reports, the strikes largely targeted energy infrastructure, reducing Ukraine’s power-generating capacity to “zero”. A civilian minibus was struck near Druzhkivka in Kindrativka village in the Donetsk region, injuring three. At least 16 civilians were killed in the Donetsk and Kherson regions.
- This followed Russian strikes targeting energy infrastructure in the Chernihiv region during the overnight hours of November 8–9, with at least 73 explosions recorded. During the overnight hours of November 5–6, Russian forces launched multiple airstrikes primarily targeting energy infrastructure in the Chernihiv region. Local authorities reported 104 explosions resulting from at least 35 strike events across 17 settlements. A power facility in a border community sustained significant damage, causing power outages and fire at the site. Additional strikes damaged transport infrastructure in the Nizhyn district and a residential building and a vehicle in the Koriukivka district.
- On November 9, Russian UAVs struck Romny, Sumy region, damaging warehouse premises of local businesses and shattering windows of a five-storey residential building.
- Also, on November 8, a Russian UAV struck a vehicle belonging to the humanitarian mission. The vehicle carried two foreign journalists from Austria and Spain and the mission’s volunteers, and no injuries were reported.
- On November 7, Russian strikes in Zaporizhzhia city led to structural damage to residential buildings and a kindergarten. During the night hours on November 7, Russian strikes hit a post office in Chuhuiv, Kharkiv region.
- Per November 6 reports, Russian strikes cut electricity to eight coal mines in the Dnipropetrovsk region, leaving approximately 2,600 miners trapped underground. On November 6, the Defence Forces of Ukraine denied claims made by the Russian forces about having seized territories in the Dnipropetrovsk and Zaporizhzhia regions.
- On November 7, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Director General Rafael Grossi stated that a local ceasefire was established near the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant to permit repairs on the damaged 330 kV “Ferrosplavna-1” power line, which had been offline for six months.
- On November 7, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy announced the launch of a program designed to protect frontline towns from Russian UAVs, including Kherson city.
- During the morning hours of November 9, Russian forces attacked the southern part of the Odesa region with UAVs. Local officials reported damage to several private garages and broken windows in a multi-story residential building. Meanwhile, on the same date, 34 Russian UAVs were intercepted in northern and eastern Ukraine.
- Per November 9 reports, Russian forces operating in the vicinity of Sumy continued to suffer losses due to desertion and inadequate training, with no tactical gains.
- On November 9, the Russian Ministry of Defense reported that its forces had captured the settlement of Volchye in the Dnipropetrovsk region. According to Russian state media, Russian forces eliminated retreating Ukrainian troops using weapons reportedly seized from Ukrainian positions in Volchye.
Crimea & Southern Ukraine
- During the night hours (local time) of November 6, units of the Special Operations Forces of the Armed Forces of Ukraine (SOF) struck Hvardiyska oil depot near the village of Gvardiysk in Russia-occupied Crimea, destroying a fuel tank and hitting two trains loaded with oil products. Additionally, the SOF destroyed an S‑400 Triumph missile launcher in the village of Uyutne near Yevpatoria and a large ammunition depot belonging to Russia in Udachne village near Simferopol.
- On November 9, ATESH, a Ukrainian Crimean Tatar partisan group, conducted a sabotage operation in the Russian-occupied Crimea region on a railway line near Simferopol, temporarily disrupting Russian military logistics by blocking train movements of ammunition, fuel, and equipment.
Other Military Developments
- On November 7, President Zelenskyy stated that Russian forces are accumulating large numbers of UAVs and preparing for new large-scale strikes against Ukraine’s critical infrastructure. Further, Zelenskyy stated that Ukraine is preparing for potential disruptions in gas supply and plans to import gas worth around two billion USD to ensure stability. He emphasized that Russia is currently not using its full strike capacity, with the ability to launch up to 500 UAVs per day and urged continued partner support.
- On November 9, President Zelenskyy stated that Ukraine plans to order 27 Patriot air defense systems from the USA while also considering borrowing similar systems from European countries.
- Russian state media, citing Russian law enforcement, reported on November 8 that at least 21,602 Ukrainian troops deserted their units in October, surpassing the May figures of 19,900.
- Following the November 8 Russian strikes against energy facilities, Ukraine’s First Deputy Minister of Energy Artem Nekrasov reported that Russia has shifted tactics to strike both electricity generation and distribution simultaneously.
Other Developments
- On November 6, the cement industry members called on the government to provide budget support instead of passing increased rail freight tariffs to businesses. They warned that a proposed 37 percent tariff hike by Ukrzaliznytsia, Ukrainian Railways, would affect the economy as two-thirds of cement produced in Ukraine is transported by rail.
- On 6 November, a court in Zaporizhzhia sentenced a Russian soldier to life in prison after finding him guilty of killing a Ukrainian Prisoner of War, who had surrendered in January 2024. The ruling is the first time Ukraine has handed down a custodial sentence for this type of war-crime charge since Russia’s 2022 invasion.
- During the night hours of November 8, Russian forces carried out a targeted attack on substations supplying Khmelnytskyi and Rivne nuclear power plants. According to Ukrainian Foreign Minister Andriy Sibiha, the infrastructure hit included key high-voltage substations, and that Russia was “deliberately jeopardizing the nuclear safety of Europe”.
- The IAEA, per November 9 reports, stated that nuclear safety in Ukraine remains critically unstable following Russian attacks. This is after the IAEA noted that two operational power plants in Khmelnytskyi and Rivne were forced to reduce electricity output after a Russian strike hit a high-voltage substation crucial to nuclear safety.
- On November 9, President Zelensky signed two decrees introducing new “special” sanctions against Russian government officials, financiers, collaborators, and propaganda entities. The measures target individuals involved in “looting” Ukrainian assets in occupied territories, spreading Russian narratives, and legitimizing their occupation.
Diplomatic and International Updates
- On November 8, Lithuanian and EU officials held discussions regarding the 20th sanctions package against Russia, which will also reportedly target Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko.
- As per November 9 reports, the ongoing US Federal Government shutdown has led to delays in weapons export to Ukraine and NATO allies, amounting to approximately five billion USD. Delays include deliveries of the HIMARS rocket system and the Aegis weapons system for military deals with Croatia, Denmark, and Poland.
- On November 7, US President Donald Trump received Hungarian President Viktor Orban in Washington and stated that there is a “very good chance” of meeting Russian President Vladimir Putin during the proposed US-Hungary summit in Budapest, Hungary. Additionally, Trump also stated his intentions of meeting Central Asian leaders at the White House as part of resolving the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Russia
- Between November 6 and 9, energy infrastructure at multiple locations was targeted by Ukrainian UAV attacks, leading to significant damage and blackouts. This included an attack on an oil refinery in Volgograd, which also killed an individual, and the Kostroma Power Station in the Kostroma Region. Airstrikes also targeted the thermal power station in Belgorod, an energy plant in Taganrog, and a petrochemical plant in the Republic of Bashkortostan. The strikes led to significant disruptions in electricity, mobile communications, and water supply services.
- Russian air defense units claimed to have shot down 75 Ukrainian UAVs across several regions during this period, most in Volgograd, and intercepted seven HIMARS rockets and over 200 UAVs between November 8–9.
- On November 8, around 10 explosions were reported in the Saratov region during early morning hours, which led to the temporary closure of the Saratov Gagarin Airport (GSV). The city has a specialized refinery facility and the Engels-2 military airbase.
- As per November 5 reports, Russia has suspended fuel exports from the Black Sea port of Tuapse, Krasnodar Krai, after a Ukrainian UAV strike significantly damaged a refinery located at the port on November 2. The strike also led to an oil spill extending over 3 kilometers from the terminal.
- Separately, reports on November 9 indicated that anti-government resistance groups destroyed four Russian military logistics facilities in late October and early November, including three communication towers in Sterlitamak and a railway control cabinet near the Vologda region. In Voronezh, three explosions caused temporary blackouts after a partisan group called ATESH reportedly shared intelligence on local energy sites with Ukrainian authorities.
- On November 4, Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a law enabling reservists, who are part of the Boyevoy Armeyskiy Rezerv Strany (BARS), a Russian military reserve force, to be trained for protecting domestic critical infrastructure, including energy and transport, against UAV attacks. Around 15 regional governments are reportedly actively recruiting reservists under the new law, and the role includes benefits related to pay and healthcare.
- Separately, on November 4, Putin signed a law for a year-round conscription, allowing military draft boards to conduct enlistment procedures, besides intakes, at any time throughout the year, starting January 2026.
- As per November 9 reports, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has approved a new security resolution sanctioning senior Russian officials, including Kirill Dmitriev, CEO of the Russian Direct Investment Fund (RDIF), and Oxana Lut, Minister of Agriculture, as well as five Russian publishing houses.
- As per November 8 reports, Zelenskyy stated that October 2025 saw the highest Russian troop losses since the start of the war, with over 25,000 soldiers killed, largely due to intensified drone strikes. Ukraine’s General Staff estimates Russia’s total losses since February 2022 at around 1.15 million personnel, along with more than 11,000 tanks and 23,000 armored vehicles.
- On November 7, Ukraine’s Foreign Ministry claimed that over 1,000 citizens from 36 African countries are serving in the Russian army, allegedly through coercion or for payment. It also reported that about 10,000 troops of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK), also known as North Korea, have been deployed near Russia’s border with Ukraine, with another 5,000 North Koreans assisting in infrastructure repairs. These reports followed talks between Russian and North Korean officials on November 6 to deepen bilateral cooperation.
Assessments & Forecast
Ukraine
- The November 8–9 Russian strikes on Ukrainian energy infrastructure are consistent with Moscow’s established strategy of degrading Ukraine’s energy generation and transmission capacity ahead of winter. The attacks followed earlier strikes on power substations and a gas processing facility on October 29–30, indicating a sustained campaign aimed at overwhelming repair capacity and destabilizing essential services. The focus on substations supplying power to nuclear facilities further highlights Russia’s intent to disrupt not only national energy output but also critical grid stability.
- FORECAST: Given reports that multiple generation sites were rendered inoperative, rolling power outages across Ukraine are expected to persist in the near term, affecting essential services such as water supply, telecommunications, and public transport. Recovery is likely to remain slow due to limited repair capacity and ongoing security risks for maintenance crews. Moscow is expected to exploit the current grid instability with renewed large-scale strikes on high-value energy nodes, including substations and gas infrastructure, to sustain civilian hardship and strain Ukraine’s emergency response capacity. As winter progresses, Russia is also likely to intensify precision strikes on distribution systems, including substations supporting nuclear power plants.
- The ongoing Russian offensive in Pokrovsk aligns with Moscow’s broader campaign to secure full control of the Donetsk region. The reported house-to-house fighting indicates that Russian forces have entered the urban perimeter, suggesting they have established a partial foothold within the city. Syrskyi’s characterization of Pokrovsk as a “continuous fortified area” underscores that Ukrainian defenses are deeply entrenched and structured to absorb prolonged attritional fighting, consistent with the defensive posture observed across other contested sectors of Donetsk since late October.
- FORECAST: Consequently, Russian forces are likely to intensify ground operations in Pokrovsk in the coming days, following current logistical buildup and forward troop rotations. The reported redeployment of up to 170,000 Russian troops to the Pokrovsk sector and the use of infiltration groups, FPV UAVs, and indirect fire indicate that Moscow is preparing for a high-intensity, multi-axis assault aimed at encircling Pokrovsk and collapsing Ukraine’s broader defensive “fortress belt” anchored around Kramatorsk and Sloviansk. Current Russian positions in the southern and eastern parts of Pokrovsk, alongside reported control of nearby settlements such as Rodynske and Myrnohrad, allow Moscow to gradually constrict Ukrainian logistics and apply sustained pressure on defensive lines. However, Russian gains will likely remain slow and attritional, constrained by heavy urban resistance, overstretched logistics, and weather-related operational limitations.
- Meanwhile, the cement industry’s warning over Ukrzaliznytsia’s proposed 37 percent rail freight tariff increase underscores broader economic risks for Ukraine’s industrial and construction sectors. As roughly two-thirds of domestic cement is transported by rail, higher tariffs would directly raise operational costs, potentially leading to moderate price increases for construction materials and reduced production rates. Similar cost pressures may emerge for other rail-dependent industries, including steel and grain producers.
Russia
- The decision to deploy reservists from the BARS to guard critical infrastructure highlights Russia’s intent to establish a specialized domestic protection force amid persistent Ukrainian UAV attacks. This development reflects ongoing manpower shortages across the Russian military, already underscored by the new law permitting year-round conscription from January 2026. The initiative appears designed to free up frontline units for offensive operations in Ukraine while ensuring continued protection of key domestic assets, particularly energy and transport infrastructure that has come under repeated attacks in recent months.
- FORECAST: While the formation of such a force demonstrates Russia’s adaptation to the evolving threat environment, the BARS program’s reliance on part-time reservists suggests that training delays, coordination challenges, and logistical shortfalls will limit the immediate operational value of this force. Moreover, integrating reservists into roles traditionally managed by security services, like Rosgvardiya and FSB, increases the risk of jurisdictional overlap and inefficiencies. As such, in the immediate-to-near term, disruptions from UAV strikes on energy and transport networks are expected to continue. Nonetheless, by mid-to-late 2026, the program is likely to enhance localized protection around high-value targets, especially in strategic regions such as Moscow, Rostov, and Belgorod, supported by improved counter-UAV systems.
- In addition to expanding reservist programs and implementing year-round conscription, Russia’s persistent manpower constraints are further evidenced by the reports of African and North Korean personnel serving with Russian forces. This aligns with Moscow’s broader strategy of sourcing manpower from allied or economically dependent states for combat, support, and intelligence roles. However, given precedent, these deployments are unlikely to deliver significant battlefield gains, as most foreign recruits lack advanced training, language compatibility, and familiarity with Russian command structures and equipment. Their roles are therefore expected to remain largely auxiliary, focused on logistics, construction, or rear-area duties.
- FORECAST: Moscow’s efforts to implement year-round conscription are likely to fuel sporadic backlash in the form of localized protests, vandalism, and arson attacks on military enlistment offices, particularly as public fatigue with the war deepens. Based on precedent, the Kremlin is expected to prioritize recruitment in economically disadvantaged regions, such as the North Caucasus, Siberia, and the Far East, where state dependence and limited employment opportunities make resistance more manageable. However, this approach also heightens the risk of localized unrest and ethnic tensions, especially in areas like Dagestan and Buryatia, which have already recorded prior instances of anti-draft demonstrations. While widespread mobilization protests remain unlikely due to tight state controls, isolated acts of defiance and sabotage against recruitment infrastructure are expected to persist through 2026.
Recommendations
Ukraine
- Avoid all travel to Ukraine due to the ongoing hostilities.
- Those operating in the East, South, and Center of Ukraine are advised to minimize outdoor travel and avoid inter-city travel due to the increase in artillery fire and airstrikes.
- Avoid all travel to Crimea due to the ongoing conflict and the potential for sporadic attacks on civilian and critical infrastructure facilities.
- Those continuing to operate in the North and West of Ukraine are advised to adhere to air raid sirens over the coming days due to the heightened threat of missile and UAV attacks by Russian forces.
- Identify the nearest shelter, which may be a Metro station, and proceed towards it when air sirens are sounded. Prepare emergency kits of food, water, medicine, and clothing in case needed.
- Considering the heightened risk of unpredictable power outages, take mitigatory measures, such as confirming that business locations have working generators, sufficient access to fuel for longer periods, and access to several flashlights. Keep necessary electronics constantly charged.
- For more information on the security situation and assistance please contact [email protected]
Russia
- Avoid nonessential travel to Russia due to potential instability in the coming days, the underlying threat of military mobilization, arbitrary detention, and increased risk of spillover violence in regions bordering Ukraine.
- Remain cognizant of authorities’ updates regarding travel prohibitions on individuals deemed eligible for military conscription.
- Foreign companies operating in Russia are advised to remain cognizant of government regulations and decrees that pose risks to business continuity and operations.
- It is recommended to have emergency plans in place in case of further deterioration in the security landscape.
- Foreign citizens in Moscow and other areas in western Russia are advised to review evacuation plans in case of emergencies.
- Avoid all travel in the vicinity of government and military facilities, as well as possible political gatherings or lone picket protests, in the coming days.
- Remain cognizant of restrictions enacted at a regional and local level.
- Avoid discussions concerning the political, economic, and military situation, even with friends and family.
- Avoid meeting strangers, discussing the political situation, or using any anti-Russia rhetoric in public.
- Those intending to travel between Russia and its neighboring European countries are advised to remain cognizant of authorities’ updates regarding land border restrictions. Review options for departing Russia, including air, rail, and land routes, with the understanding that certain options may become unavailable with short notice.